Intermittent Fasting for Digestive Health: Heal Your Gut Naturally
Intermittent fasting for digestive health: A guide to heal your gut in a natural way in 2025

Suppose you're struggling with bloating, acid reflux, irregular bowel movements, or chronic digestive discomfort. In that case, the solution might not be adding more to your diet—it could be giving your digestive system strategic breaks through intermittent fasting (IF). This ancient practice is revolutionizing modern digestive health, and the science behind it is nothing short of remarkable.
Your gut works 24/7 to process food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. But when does it get time to repair, reset, and restore?
That's where intermittent fasting comes in, offering your digestive system the rest it desperately needs to function optimally.
The Digestive Health Crisis
Why Your Gut Needs a Break
Americans are experiencing unprecedented levels of digestive distress. Recent data reveals alarming trends:
- 74% of Americans live with digestive discomfort weekly
- 60-70 million Americans are affected by digestive diseases
- IBS affects 10-15% of the US population, with symptoms worsening in modern lifestyles
- GERD impacts over 20% of American adults, with rates increasing annually
- The average American eats every 2-3 hours, never giving their digestive system a true break
Our ancestors naturally fasted between meals due to food scarcity, but modern society's constant eating pattern has disrupted our digestive rhythms. The body clock works in synchrony with changing daily cyclical fluctuations in diversity, and intermittent fasting helps restore these natural patterns.
What Is Intermittent Fasting and How Does It Heal Digestion?
Intermittent fasting isn't about what you eat—it's about when you eat. By cycling between periods of eating and fasting, you allow your digestive system to complete essential maintenance tasks it can't perform while constantly processing food.
The Digestive Magic of Fasting
1. Migrating Motor Complex (MMC) Activation During fasting periods, your digestive system activates the MMC—powerful waves of muscle contractions that sweep undigested food particles and bacteria from your small intestine into your colon. Fasting allows the gut's natural cleaning process (the migrating motor complex) to do its job, reducing bloating and discomfort.
2. Gut Microbiome Rebalancing Intermittent fasting (IF) is a promising paradigm for weight loss, which has been shown to modulate the gut microbiota. Research demonstrates that 16 bacterial genera change their abundance in response to intermittent fasting, promoting beneficial bacteria while reducing harmful strains.
3. Intestinal Barrier Repair Fasting periods allow your intestinal lining to repair microscopic damage, reducing intestinal permeability (leaky gut) and decreasing inflammation throughout your digestive tract.
4. Digestive Enzyme Optimization Regular fasting helps regulate digestive enzyme production, improving your ability to break down and absorb nutrients when you do eat.
The Science: How Intermittent Fasting Transforms Your Gut
Groundbreaking Research Findings
Recent studies have revealed profound effects of intermittent fasting on digestive health:
Microbiome Diversity Enhancement Protein pacing and intermittent fasting improve gut symptomatology and microbial diversity, with participants showing increased beneficial bacteria within just three weeks of starting an IF protocol.
Inflammation Reduction: Intermittent fasting is essentially a cleansing activity in terms of health. Especially since its applications that exceed 16 h trigger autophagy, helping reduce chronic inflammation in the digestive tract.
Gut Hormone Regulation
Fasting periods help regulate key digestive hormones, including ghrelin (hunger hormone), leptin (satiety hormone), and GLP-1 (glucose regulation), creating better appetite control and digestive timing.
Acid Reflux Improvement
Intermittent fasting may reduce acid exposure time and improve symptoms for individuals with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), with studies showing significant symptom reduction in just four weeks.
Types of Intermittent Fasting
Finding Your Digestive Sweet Spot
1st Method: 16:8 Method (Beginner-Friendly)
Schedule: 16 hours fasting, 8-hour eating window
Example: Eat between 12 PM - 8 PM, fast from 8 PM to 12 PM the next day
Best For: Beginners, busy professionals, those with mild digestive issues
Digestive Benefits:
- Allows 2-3 MMC cycles during the fasting period
- Reduces late-night eating (major GERD trigger)
- Easy to maintain long-term
- Minimal digestive adjustment period
2nd Method: 14:10 Method (Gentle Start)
Schedule: 14 hours fasting, 10-hour eating window
Example: Eat between 10 AM - 8 PM, fast from 8 PM to 10 AM the next day
Best For: Women (hormonal considerations), those with eating disorders, seniors
Digestive Benefits:
- Gentler introduction to fasting
- Still allows significant MMC activation
- Reduces evening digestive burden
- Suitable for those with blood sugar sensitivity
3rd Method: 18:6 Method (Advanced)
Schedule: 18 hours fasting, 6-hour eating window
Example: Eat between 2 PM - 8 PM, fast from 8 PM - 2 PM the next day
Best For: Experienced fasters, those with significant digestive issues, and weight loss goals
Digestive Benefits:
- Maximum MMC activation time
- Deep autophagy for cellular repair
- Significant microbiome rebalancing
- Enhanced digestive enzyme sensitivity
4th Method: One Meal a Day (OMAD) (Expert Level)
Schedule: 23 hours fasting, 1-hour eating window
Example: One large meal per day, typically dinner
Best For: Experienced fasters only, under medical supervision
Digestive Benefits:
- Maximum digestive rest period
- Profound gut microbiome changes
- Complete the MMC cycle completion
- Caution: May be too extreme for many digestive conditions
5th Method: 5:2 Method (Flexible Approach)
Schedule: Normal eating 5 days, very low calories (500-600) for 2 days
Example: Regular diet Monday-Friday, fasting days on Tuesday/Thursday
Best For: Social eaters, those preferring weekly rather than daily restrictions
Digestive Benefits:
- Periodic deep digestive rest
- Flexible social eating
- Microbiome diversity improvements
- Reduced weekly digestive burden
Intermittent Fasting for Specific Digestive Conditions
IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome)
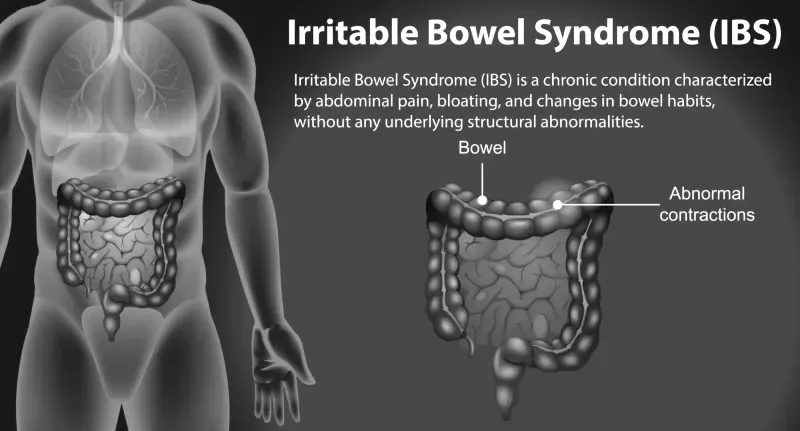
Recommended Method: 16:8 or 14:10 Key Benefits:
- Regulating digestion: Fasting allows the gut's natural cleaning process (the migrating motor complex) to do its job, reducing bloating and discomfort
- Reduces the fermentation time of trigger foods
- Helps identify food sensitivities during eating windows
- Decreases gut hypersensitivity
Protocol Tips:
- Start with 12:12 and gradually extend the fasting window
- Focus on low-FODMAP foods during eating windows
- Stay hydrated during fasting periods
- Consider electrolyte supplementation
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
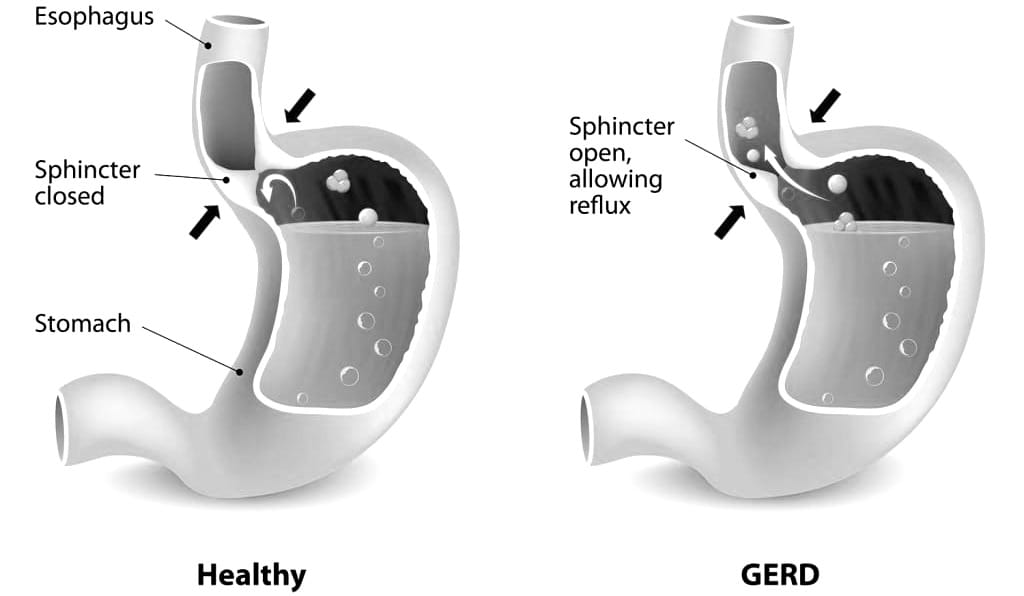
Recommended Method: 16:8 with an early eating window
Key Benefits:
- For people with GERD, not eating later at night (before lying down for bed) may help reduce acid reflux. So, intermittent fasting practices may help with GERD in this way
- Reduces late-night acid production
- Allows stomach emptying before sleep
- Decreases overall acid exposure time
Protocol Tips:
- End eating window 3-4 hours before bedtime
- Start eating window later in the morning (natural acid is lower)
- Focus on alkaline foods during eating periods
- Avoid trigger foods even during eating windows
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
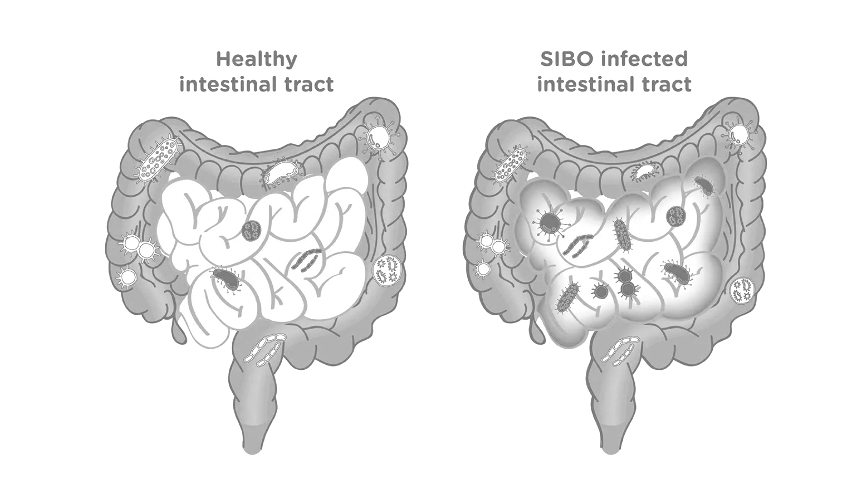
Recommended Method: 18:6 or longer periods
Key Benefits:
- Starves excess bacteria during fasting periods
- Allows MMC to sweep bacterial overgrowth downward
- Reduces bacterial fermentation and gas production
- Helps reset gut microbiome balance
Protocol Tips:
- Consider longer fasting windows (18+ hours)
- Work with a healthcare provider familiar with SIBO
- May need to adjust based on SIBO type (hydrogen vs. methane)
- Monitor symptoms carefully during transition
Inflammatory Bowel Conditions
Recommended Method: 14:10 or 16:8 (gentle approach)
Key Benefits:
- Reducing inflammation through autophagy activation
- Gives inflamed tissues time to heal
- Reduces dietary triggers and irritants
- May help modulate immune response
Protocol Tips:
- Start very gradually (12:12 initially)
- Work closely with a gastroenterologist
- Focus on anti-inflammatory foods during eating windows
- Monitor for any symptom worsening
Your Complete Intermittent Fasting Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Preparation (Week 1)
Goal: Prepare your body and mind for fasting success
Daily Actions:
- Eliminate processed foods from your current diet
- Increase water intake to 8-10 glasses daily
- Practice mindful eating by eliminating distractions during meals
- Establish consistent meal timing (even if not fasting yet)
- Reduce caffeine if you consume more than 2 cups daily
Digestive Prep:
- Take digestive enzymes with meals if you have poor digestion
- Include prebiotic foods (garlic, onions, asparagus) to support beneficial bacteria
- Limit sugar and refined carbs to reduce harmful bacteria
Phase 2: Gentle Introduction (Weeks 2-3)
Goal: Begin with 12:12 fasting and assess your response
Week 2 Schedule:
- Fasting Window: 8 PM - 8 AM (12 hours)
- Eating Window: 8 AM - 8 PM (12 hours)
- Focus: Stop eating 3 hours before bedtime
Week 3 Schedule:
- Fasting Window: 8 PM - 10 AM (14 hours)
- Eating Window: 10 AM - 8 PM (10 hours)
- Focus: Extend morning fast gradually
What to Expect:
- Initial hunger pangs (normal, will subside)
- Possible mild headaches (stay hydrated)
- Improved morning mental clarity
- Better sleep quality from no late-night eating
Phase 3: Optimization (Weeks 4-8)
Goal: Establish your optimal fasting window and maximize benefits
16:8 Schedule (Most Popular):
- Fasting Window: 8 PM - 12 PM (16 hours)
- Eating Window: 12 PM - 8 PM (8 hours)
- Meals: Lunch (12 PM), Snack (3 PM), Dinner (6-7 PM)
Advanced Options:
- 18:6: Eating window 2 PM - 8 PM
- 20:4: Eating window 4 PM - 8 PM
- Alternate days: Vary fasting windows based on schedule
Phase 4: Long-term Success (Week 8+)
Goal: Maintain consistent practice with flexibility for life
Lifestyle Integration:
- Adjust fasting windows for social events
- Maintain consistency 5-6 days per week
- Listen to your body's hunger and satiety cues
- Continue monitoring digestive improvements
What to Eat and Drink During Your Fasting and Eating Windows
During Fasting Windows: What's Allowed
✅ Approved Fasting Beverages:
- Plain water (add lemon for flavor)
- Black coffee (no cream, sugar, or artificial sweeteners)
- Plain tea (green, black, herbal - unsweetened)
- Sparkling water (unflavored)
- Apple cider vinegar water (1-2 tsp in water for digestive support)
- Bone broth (some protocols allow, under 50 calories)
❌ Fasting Window Violations:
- Any beverages with calories
- Artificial sweeteners (may trigger digestive responses)
- Gum or mints (even sugar-free)
- Supplements in pill form (take during eating windows)
During Eating Windows: Optimizing Digestive Health
First Meal Strategy (Break Your Fast):
- Start gentle: Begin with easily digestible foods
- Hydrate first: Drink 16-20oz of water 30 minutes before eating
- Include probiotics: Kefir, yogurt, or probiotic supplements
- Add digestive support: Consider digestive enzymes if needed
Optimal Food Choices:
Gut-Healing Proteins:
- Grass-fed beef and lamb
- Wild-caught fish (salmon, sardines, mackerel)
- Pasture-raised eggs
- Bone broth
- Collagen powder
Prebiotic-Rich Vegetables:
- Asparagus, artichokes, onions, garlic
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, arugula)
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower)
- Root vegetables (sweet potatoes, carrots)
Healthy Fats for Hormone Production:
- Avocados and avocado oil
- Olive oil (extra virgin, cold-pressed)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia, flax)
- Coconut oil and coconut products
Anti-Inflammatory Spices:
- Turmeric and ginger
- Cinnamon and cardamom
- Oregano and thyme
- Black pepper and cayenne
Top 5 Intermittent Fasting Support Products for Digestive Health
1. LMNT Electrolyte Drink Mix

Expert Rating: 4.8/5 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Essential for maintaining proper hydration and preventing fasting-related headaches and fatigue.
Pros:
- Zero calories, won't break your fast
- Optimal sodium, potassium, magnesium ratio
- No artificial ingredients or fillers
- Multiple flavor options
- Developed by keto and fasting experts
- Prevents common fasting side effects
Cons:
- Higher price point than generic electrolytes
- Strong salty taste (may need an adjustment period)
- Limited availability in physical stores
Best For: Anyone practicing IF longer than 16 hours, those experiencing fasting fatigue or headaches.
2. Thorne Digestive Enzymes

Expert Rating: 4.7/5 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Helps optimize digestion during eating windows, especially important when meal frequency is reduced.
Pros:
- Comprehensive enzyme blend for all macronutrients
- Third-party tested for purity and potency
- NSF certified for quality assurance
- Helps prevent digestive discomfort from larger meals
- Supports nutrient absorption
- Trusted by healthcare professionals
Cons:
- Must be taken with meals (not during fasting)
- More expensive than basic enzyme formulas
- Large capsule size
Best For: People with digestive issues transitioning to IF, those eating larger meals during compressed eating windows.
3. Garden of Life Dr. Formulated Probiotics Once Daily

Expert Rating: 4.6/5 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Supports gut microbiome balance, which is crucial during the dietary changes associated with intermittent fasting.
Pros:
- 30 billion CFU with 14 clinically studied strains
- Shelf-stable (no refrigeration required)
- Delayed-release capsules protect against stomach acid
- Organic, non-GMO ingredients
- Specifically formulated to survive fasting periods
- Includes prebiotic fiber for enhanced effectiveness
Cons:
- Should be taken during the eating window
- Some users experience initial bloating
- Premium pricing reflects quality ingredients
Best For: Supporting gut health transformation during IF, those with a history of antibiotic use with digestive sensitivities.
4. Bulletproof Brain Octane C8 MCT Oil
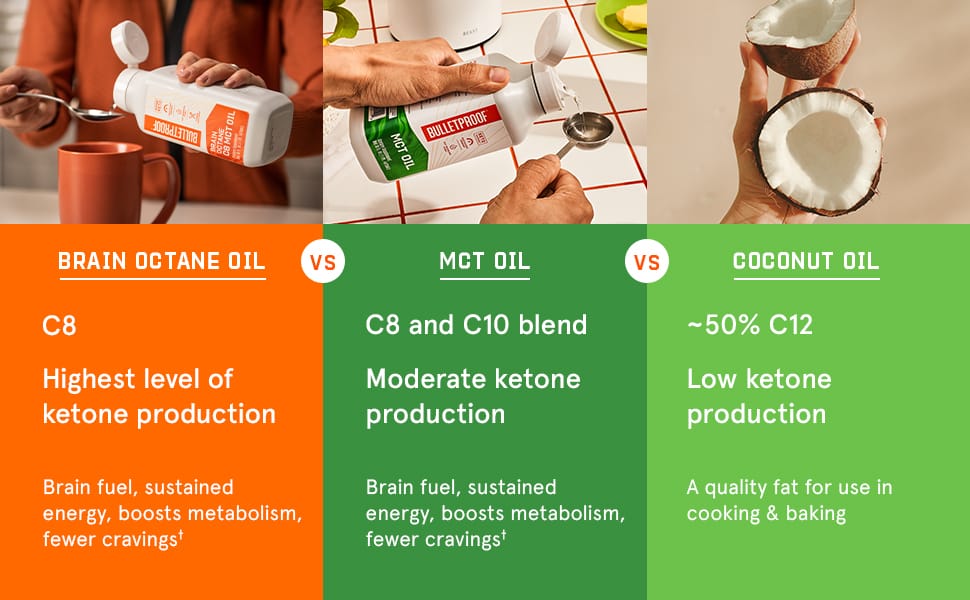
Expert Rating: 4.5/5 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Pure C8 MCT oil that can enhance mental clarity during fasting while supporting ketone production for digestive benefits.
Pros:
- Pure C8 caprylic acid (most effective MCT)
- Rapidly converts to ketones for brain fuel
- May help reduce fasting hunger pangs
- Supports beneficial bacteria growth
- Odorless and tasteless
- Can be added to coffee without breaking fast (small amounts)
Cons:
- Can cause digestive upset if too much is used initially
- Higher cost than mixed MCT oils
- Technically breaks a "pure" fast (though minimal impact)
Best For: Experienced fasters looking to enhance mental clarity, those transitioning from eating frequently to fasting.
5. Pure Encapsulations Digestive Enzymes Ultra

Expert Rating: 4.4/5 ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Comprehensive digestive support for optimal nutrient breakdown during compressed eating windows.
Pros:
- Broad-spectrum enzyme formula
- Includes betaine HCl for stomach acid support
- Hypoallergenic and free from common allergens
- Physician-recommended brand
- Supports digestion of all food types
- Third-party tested for purity
Cons:
- Expensive compared to basic enzyme supplements
- Multiple capsules needed per meal
- Must be taken with food (not during fasting)
Best For: People with low stomach acid, those experiencing digestive discomfort with larger IF meals, and individuals with multiple food sensitivities.
Troubleshooting Common Intermittent Fasting Digestive Issues
Issue 1: Increased Hunger and Cravings
Symptoms: Intense hunger during fasting windows, obsessive food thoughts. Timeline: Usually improves within 1-2 weeks
Solutions:
- Increase water intake during fasting (aim for 12-16oz upon waking)
- Add a pinch of sea salt to water for electrolyte balance
- Keep busy during typical meal times
- Practice deep breathing or meditation when cravings hit
- Ensure adequate protein and healthy fats during eating windows
When to Be Concerned: If hunger is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, or doesn't improve after 2 weeks.
Issue 2: Digestive Discomfort When Breaking Fast
Symptoms: Nausea, bloating, or cramping with the first meal.
Timeline: Usually resolves within 1 week of adjustment
Solutions:
- Start with smaller portions and eat slowly
- Begin with easily digestible foods (bone broth, cooked vegetables)
- Take digestive enzymes with your first meal
- Chew thoroughly and eat mindfully
- Avoid raw vegetables or high-fat foods immediately after fasting
Prevention Strategy: Gradually increase fasting windows rather than jumping to long periods immediately.
Issue 3: Constipation During Fasting
Symptoms: Reduced bowel movement frequency, harder stools
Timeline: May occur in the first 2-4 weeks
Solutions:
- Increase water intake significantly (add 2-4 additional glasses)
- Add a magnesium supplement (200-400mg) during the eating window
- Include more fiber-rich foods during eating periods
- Consider psyllium husk or other gentle fiber supplements
- Light movement or walking during fasting windows
Medical Consultation: If constipation persists beyond 1 week or is severe.
Issue 4: Acid Reflux or Heartburn
Symptoms: Burning sensation in the chest, especially when lying down
Timeline: May worsen initially but typically improves within 2-3 weeks
Solutions:
- End eating window 3-4 hours before bedtime
- Avoid trigger foods (spicy, acidic, high-fat) even during eating windows
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals within your eating window
- Sleep with your head elevated
- Consider apple cider vinegar (1 tsp in water) during fasting
Modification: Shorter fasting windows (14:10) may be better for severe GERD.
Issue 5: Low Energy or Brain Fog
Symptoms: Fatigue, difficulty concentrating, mood changes
Timeline: Usually improves within 3-7 days
Solutions:
- Ensure adequate electrolyte intake (sodium, potassium, magnesium)
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule (7-9 hours)
- Avoid strenuous exercise during the initial adaptation period
- Consider shorter fasting windows initially
- Ensure adequate calories during eating windows
Red Flags: Severe weakness, persistent dizziness, or symptoms lasting beyond 2 weeks require medical evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Intermittent Fasting for Digestive Health
1. Can intermittent fasting cure digestive disorders like IBS or GERD?
While intermittent fasting can significantly improve symptoms of many digestive conditions, it's not a "cure" in the traditional sense. Fasting allows the gut's natural cleaning process (the migrating motor complex) to do its job, reducing bloating and discomfort, and research shows it can provide substantial symptom relief.
For IBS: Studies indicate 60-80% of people experience reduced bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements within 4-8 weeks of consistent IF practice. The improvement comes from giving the digestive system regular breaks and allowing proper motility patterns to resume.
For GERD: Intermittent fasting may reduce acid exposure time and improve symptoms for individuals with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), with many people experiencing a 40-60% reduction in symptoms when practiced correctly.
Important Note: IF should complement, not replace, medical treatment for serious digestive disorders. Always work with your healthcare provider to create a comprehensive treatment plan.
2. How long does it take to see digestive improvements with intermittent fasting?
The timeline for digestive improvements varies based on your starting health and chosen fasting method:
Week 1-2: Initial adaptation phase
- Reduced late-night digestive discomfort
- Better sleep quality from not eating before bed
- Some people notice reduced bloating
Week 3-4: Gut microbiome begins shifting
- Balancing the microbiome: A fasting period encourages the growth of beneficial gut bacteria
- Improved regularity and bowel movement quality
- Reduced gas and bloating for most people
Week 4-8: Significant improvements are typically seen
- Enhanced digestive enzyme function
- Better appetite regulation
- Noticeable improvement in chronic digestive symptoms
Month 3+: Long-term benefits stabilize
- Sustained improvements in gut microbiome diversity
- Enhanced digestion and nutrient absorption
- Reduced inflammation markers
Individual Variation: People with more severe digestive issues may need 8-12 weeks to see maximum benefits, while those with minor issues might notice improvements within 2-3 weeks.
3. Is it safe to take supplements and medications during fasting windows?
Medications: Never stop prescribed medications without consulting your healthcare provider. Most medications can and should be continued during IF:
Safe During Fasting:
- Most prescription medications (unless specifically required with food)
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) - though better absorbed with food
- Medications for chronic conditions (blood pressure, diabetes, etc.)
Better With Food (Take During Eating Windows):
- Digestive enzymes
- Probiotics
- Iron supplements
- Some antibiotics
- NSAIDs (to prevent stomach irritation)
Supplements During Fasting: Most supplements won't break your fast, but timing matters for effectiveness:
- Electrolytes: Essential during longer fasts (16+ hours)
- Magnesium: Can be taken anytime, may help with fasting-related constipation
- B vitamins: Better absorbed with food, but won't break fast
- Protein powders: Will break your fast due to calorie content
Consult Your Doctor: If you take diabetes medications, blood pressure medications, or have any chronic health conditions, work with your healthcare provider to adjust timing and dosing as needed.
4. Can women practice intermittent fasting safely? What about hormonal considerations?
Women can absolutely practice intermittent fasting safely, but hormonal considerations require special attention:
Female-Specific Benefits:
- Improved insulin sensitivity
- Better digestive hormone regulation
- Reduced PMS-related digestive issues
- Enhanced gut microbiome diversity
Hormonal Considerations:
- Menstrual cycle: Some women find IF affects their cycle initially, usually normalizing within 2-3 months
- Reproductive hormones: Very restrictive fasting (OMAD, multi-day fasts) may disrupt reproductive hormones
- Stress response: Women may be more sensitive to fasting as a stressor
Recommended Approach for Women:
- Start gradually: Begin with 12:12, progress to 14:10, then 16:8 if desired
- Listen to your body: If you experience cycle irregularities, consider shorter fasting windows
- Adequate nutrition: Ensure sufficient calories and nutrients during eating windows
- Cycle syncing: Some women find varying fasting windows with menstrual cycle phases helpful
- Pregnancy/breastfeeding: Avoid IF during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Red Flags: Stop IF and consult a healthcare provider if you experience: missed periods, extreme fatigue, hair loss, or signs of eating disorder behaviors.
5. What should I do if intermittent fasting makes my digestive symptoms worse?
If IF initially worsens digestive symptoms, don't panic—this is often temporary as your body adjusts. However, proper modification is important:
Temporary Worsening (Normal Adaptation):
- Increased hunger and food obsession (1-2 weeks)
- Changes in bowel movement patterns (1-3 weeks)
- Initial bloating when breaking fast (1 week)
- Mild fatigue or mood changes (3-7 days)
Concerning Symptoms (Require Modification or Medical Consultation):
- Severe abdominal pain
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Significant weight loss (>2 lbs/week)
- Worsening of pre-existing digestive conditions after 2+ weeks
- Signs of disordered eating behaviors
Modification Strategies:
Step 1: Reduce fasting window
- Move from 16:8 to 14:10 or 12:12
- Ensure adequate nutrition during eating windows
Step 2: Adjust food choices
- Eliminate potential trigger foods
- Focus on easily digestible foods when breaking fast
- Consider food sensitivity testing
Step 3: Address underlying issues
- Consider SIBO testing if bacterial overgrowth is suspected
- Evaluate for food intolerances
- Check for underlying digestive conditions
Step 4: Professional guidance
- Work with a registered dietitian experienced in IF
- Consult a gastroenterologist for persistent symptoms
- Consider a functional medicine approach for comprehensive evaluation
Remember: IF should improve your digestive health and quality of life. If it consistently makes you feel worse after appropriate adjustments, it may not be the right approach for your current health status.
Key Takeaways
Your Path to Digestive Wellness Through Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting represents one of the most powerful, natural approaches to healing and optimizing your digestive health. By giving your gut the regular rest it needs, you're not just treating symptoms—you're addressing the root cause of many modern digestive issues.
Essential Points to Remember:
🎯 Start Gradually: Begin with 12:12 fasting and slowly extend your fasting window as your body adapts. Rushing the process can cause unnecessary digestive distress and reduce long-term success.
⏰ Consistency Trumps Perfection: Practicing IF 5-6 days per week with occasional flexibility for social events is more sustainable and effective than perfect adherence followed by complete abandonment.
🥗 Quality Matters During Eating Windows: During your eating windows, make sure you eat a variety of nutrient-rich foods that support your digestive health goals. IF isn't permission to eat poorly during non-fasting hours.
💧 Hydration is Non-Negotiable: Proper hydration with electrolyte balance prevents the Suppose you're struggling with bloating, acid reflux, irregular bowel movements, or chronic digestive discomfort. In that case, the most common IF side effects support the natural detoxification processes occurring during fasting.
📊 Track Your Progress: Monitor digestive symptoms, energy levels, sleep quality, and overall well-being to understand how IF is affecting your individual health profile.
🩺 Medical Partnership: Work with healthcare providers familiar with intermittent fasting, especially if you have pre-existing digestive conditions or take medications.
The Long-Term Vision:
The gut microbiome composition returns to baseline upon cessation of TRF, which means the benefits of IF require ongoing practice. This isn't a short-term fix—it's a sustainable lifestyle approach that can provide lasting digestive wellness.
Your digestive system has a remarkable capacity for healing when given the proper conditions. Through strategic fasting periods, you're providing your gut with the time and space it needs to repair, rebalance, and restore optimal function.
The journey to digestive wellness through intermittent fasting is personal and unique. Some people experience rapid improvements within weeks, while others need months to see significant changes. The key is patience, consistency, and listening to your body's signals along the way.
By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide—starting gradually, choosing the right fasting method for your lifestyle, optimizing your eating windows with gut-healthy foods, and monitoring your progress—you're setting yourself up for long-term digestive success.
Remember: intermittent fasting isn't just about changing when you eat; it's about transforming your relationship with food, improving your body's natural rhythms, and unlocking your digestive system's incredible healing potential. Your gut has been waiting for this opportunity to heal—now you know how to give it exactly what it needs.